Average home septic system
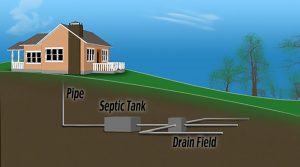
Pipe – All of the homes waste water exits through this pipe and into the septic tank.
Septic Tank – The Septic tank or holding tank is a watertight container that is buried about 10-15ft from the home. They are made out of various materials such as fiberglass, polyethylene or concrete. Holding tanks are designed to separate water, solids, and oils
Drain Field – After the septic tank has separated the solids and the oils the remaining sewage will be sent to the drain field. From there it will be distributed and allowed to seep back into the ground to allow the soil to filter out harmful bacteria and waste.
Septic Tank

Inspection Access – By removing these covers the tank can be properly inspected and pumped. It is recommended that you have your tank pumped and inspected often for blockage, cracks and other malfunctions. Catching a problem early will save money. damages caused by neglect will become far more expensive than routine inspections.
Scum – Grease and oils that enter the tank will rise to the top of the sewage and form a layer that is referred to as “Scum”.
Inlet Baffle – The inlet baffle is designed to prevent sewage from flowing back through the pipe and into the home.
Outlet Baffle – The outlet baffle prevents debris from flowing into the leach field.
Liquid sewage – Liquid Sewage or wastewater is what is left after the oil and solids have separated. This liquid will exit through the outlet baffle and into the drain field where it will be further processed.
Sludge solids – The “Sludge” is made up from solids that have exited the home. Sludge will only partially decompose and the remains will need to be pumped out approximately every 3-5 years depending on usage.
Drain field
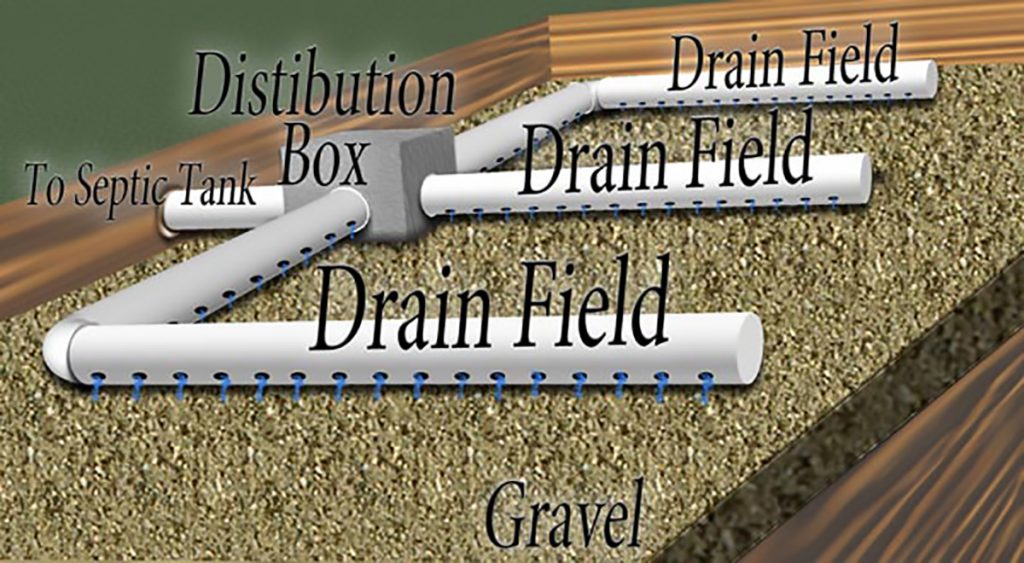
Distribution Box – Sewage enters the drainage box and is distributed to each portion of drain field. The sewage is spread out so that one area of soil doesn’t become overwhelmed, therefore, becoming ineffective.
To septic tank – Usually 4 inches in diameter; this pipe is used to deliver the sewage from the septic tank to the distribution box.
Drain Field – The drain field is a series of four-inch pipes with perforated bottoms where the sewage will finally exit the system and slowly seep into the soil. The soil will naturally purify the sewage and remove harmful viruses, bacteria’s, and diseases. The remaining liquid will either evaporate or return to an underground water source.
Gravel – A typical drain field will sit on top of a layer of gravel that is one to, one and a half feet deep. Gravel is used in order to ensure proper drainage of the sewage.
